DataJoin Concepts
Applications must be able to work with Natural Language.
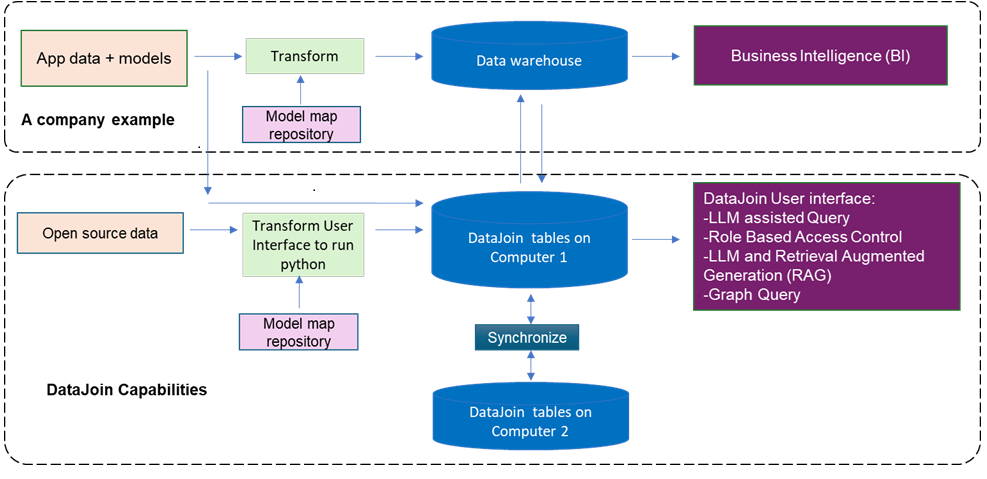




Almost Language Model (ALM)
Language is the Model for all other models.
There are problems with applications' underlyig data models. Data models are too complex for non IT persons. Data models are too restrictives (rigid) for changing needs. Therefore, communication between people occurs using office document format such as word, excel, PowerPoint and pdf.
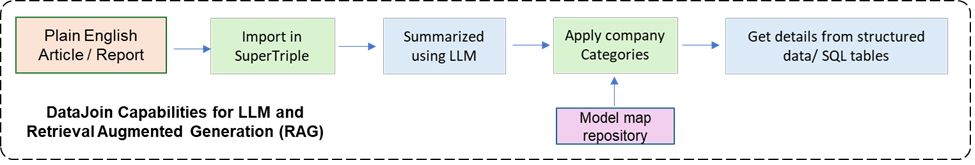
ALM can be used to ask questions to your Application data using chatGPT natural language engine (RAG-Retrieval Augmented Generation).
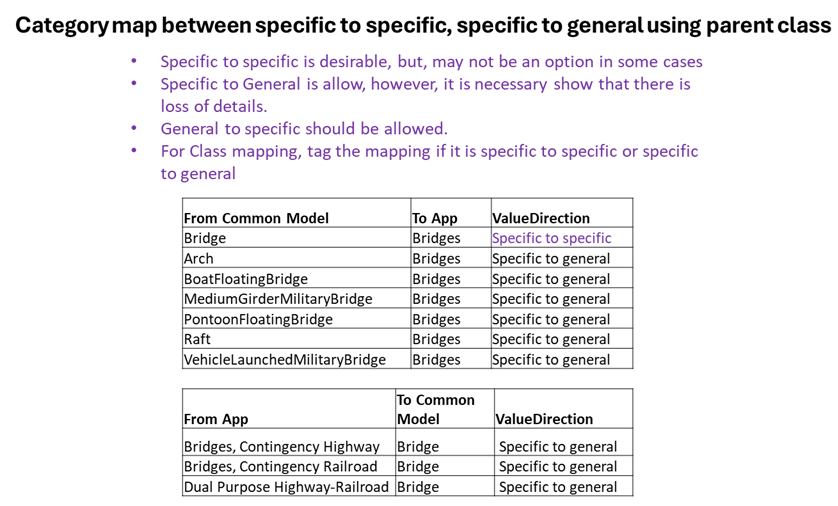
* Last column build the field separator as "|". Copy paste the rows in the last column for import
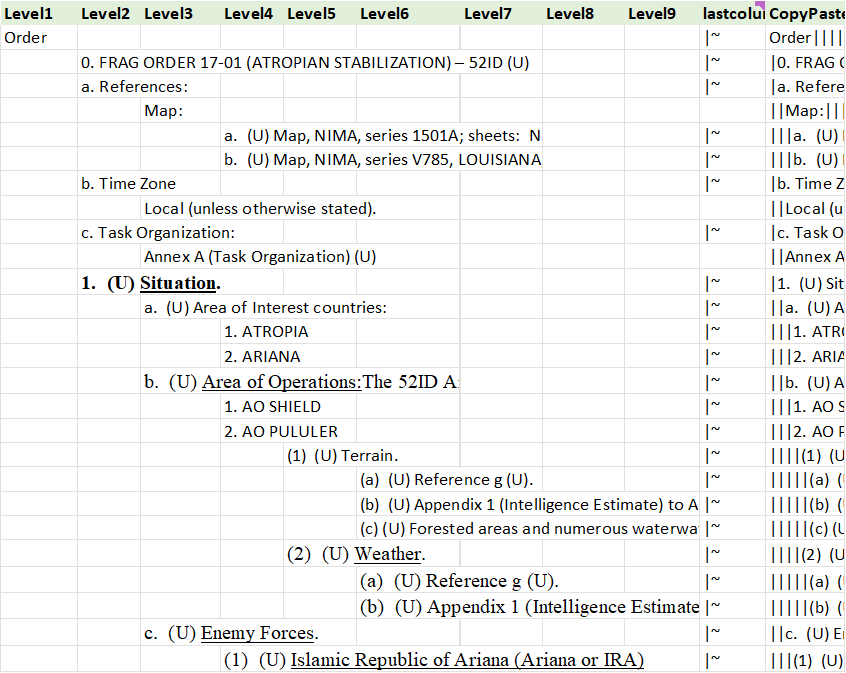
* Last column build the field separator as "|". Copy paste the rows in the last column for import
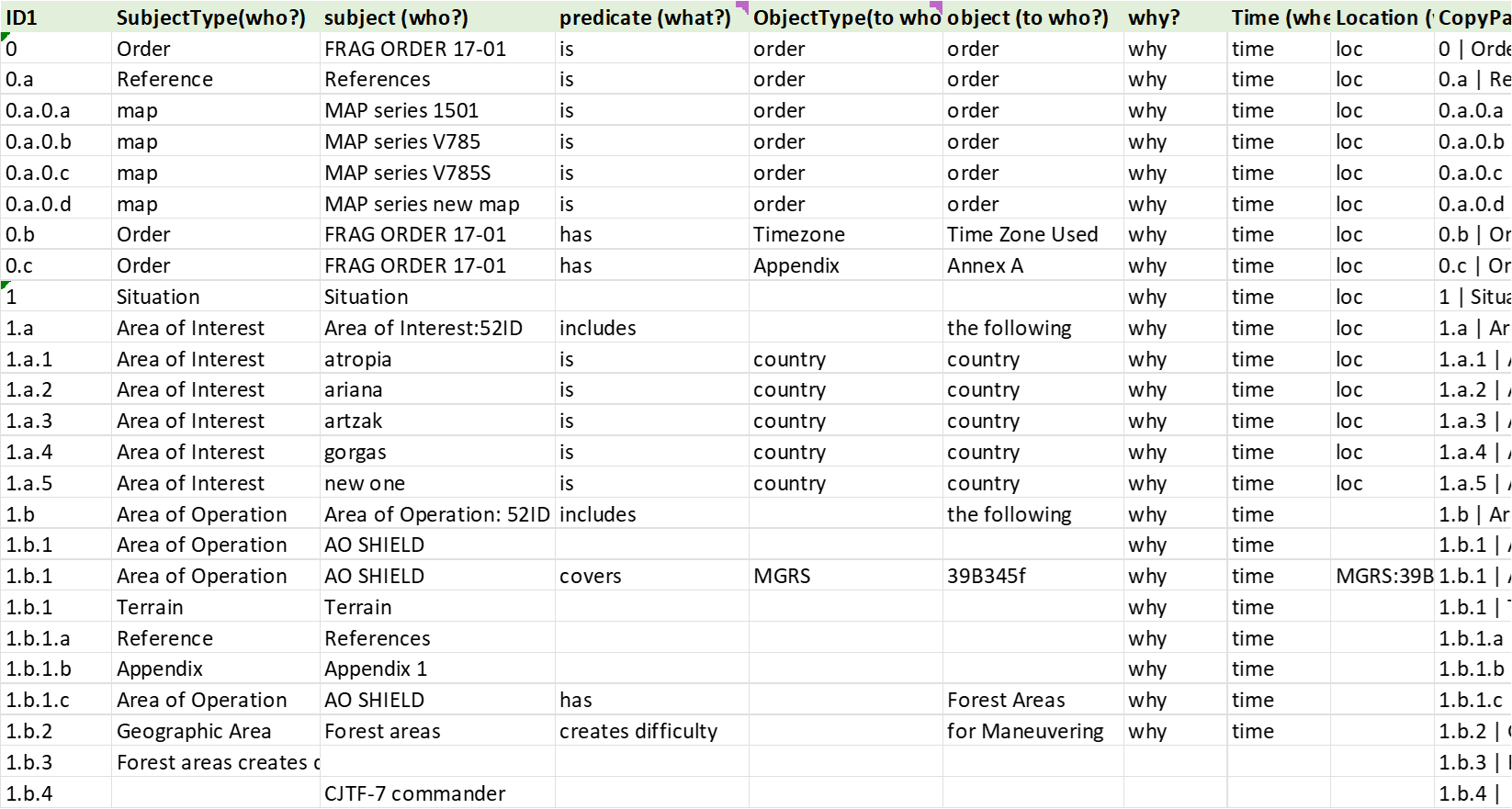
* Classes/ Entities are extracted from day to day communications documents such as email, pdf, word, excel, etc.
* Defined classes/entities can be used during data entry, however, it is not mandatory.
* It is allow to have multiple terms referring to same Class.
* Data type such as interger or numeric are suggestions and they are not enforced.
* Entity attributes have predicate to explain it relationship to the entity. For example, Person entity can have country attribute but, it is further explained predicate such as “hascitizenship of”.
* Attribute and relationship are different. For example, Person has weight and height as attribute. Person “has citizenship of” is relationship to the country.
* Multiple entry of the same attribute is allowed. It simply indicates that a person has two names or two hair colors or two driver’s licenses.
* Logical and or Physical data models may have hundreds of entities and thousands of attributes
* Even after large entitities and relationship define, there can be manay more still be defined
* In some domains / applications, data model can never catch up with terms used in communciation using word, excel, powerpoint and pdf.
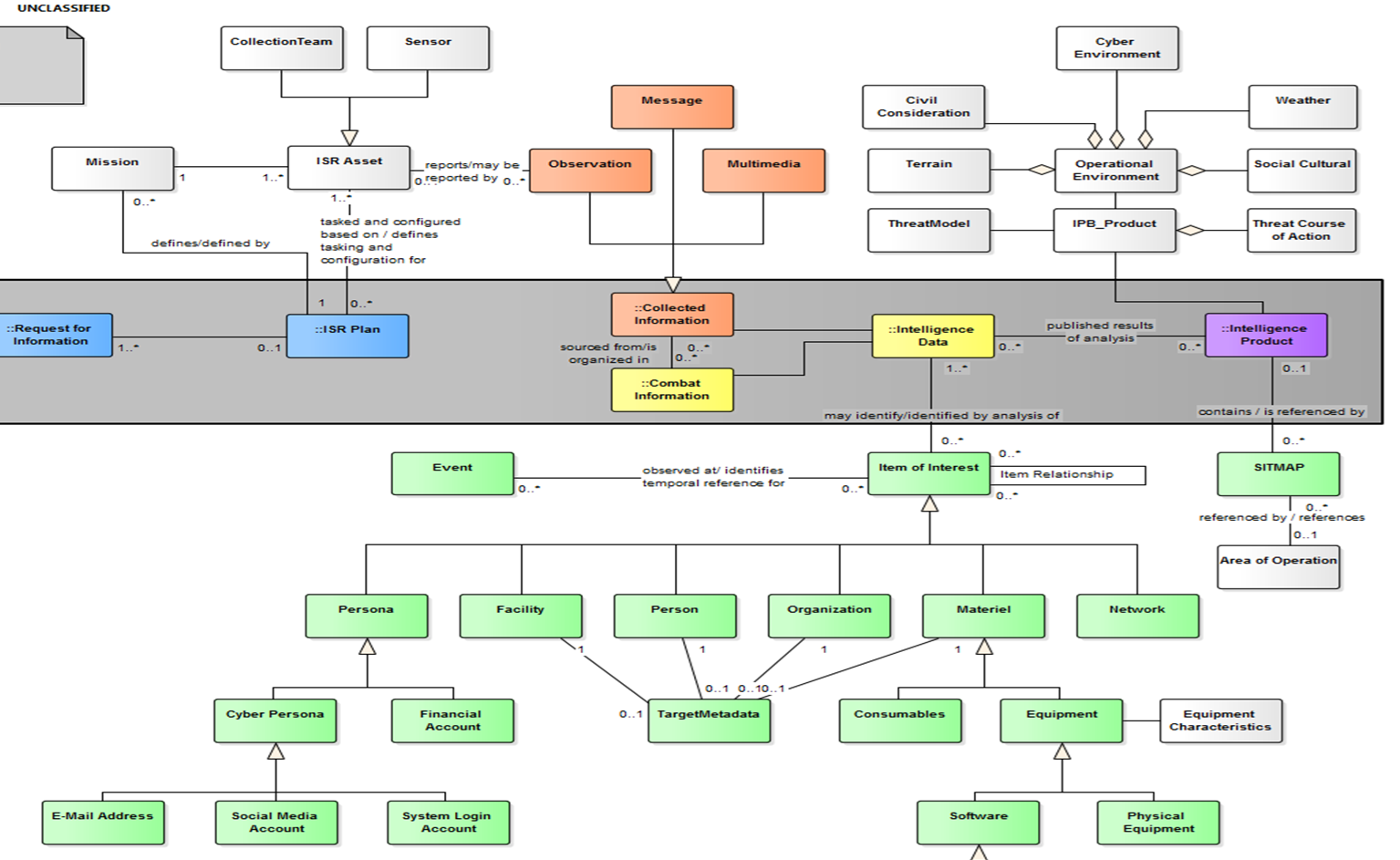
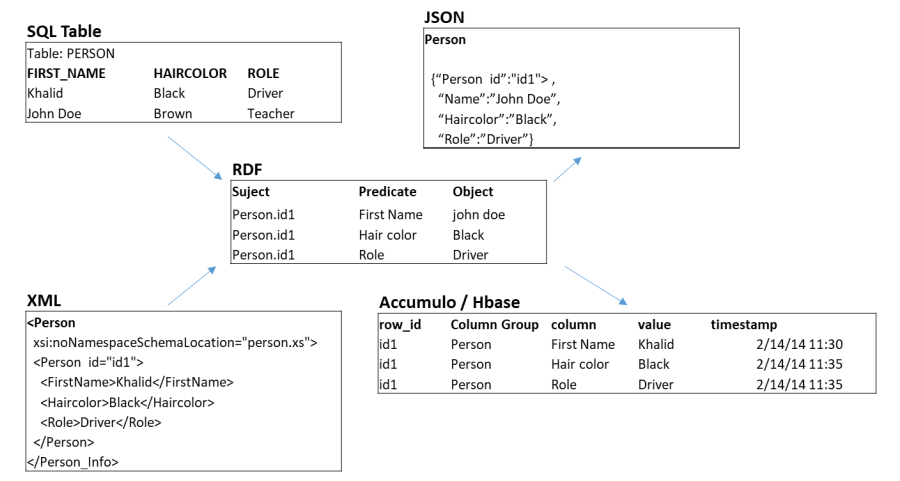
* SQL table models: An entity and its attribute are a table and columns. Entity to Entity relation is foreign key in a table pointing to another table.
* JSON or XML object can have entities, attributes and its relationship all in one object.
* It is necessary to show terms used by a user is mapped to a legacy model, otherwise, users would not be allowed to use natural language.
* If a natural language is used without mapping to legacy model, then the natural language model would become another isolated model with yet another integration effort.
* Side by side view is type of "value mappping". Thus, there is schema to schema mapping needed for actual transformation.
* ETL (Extract Trasnform and Load) has steps such as: Structure / Schema mapping, transform value formats using global standars (date, time, geo cordincates, Units of Measurement), value transform using mapping table.
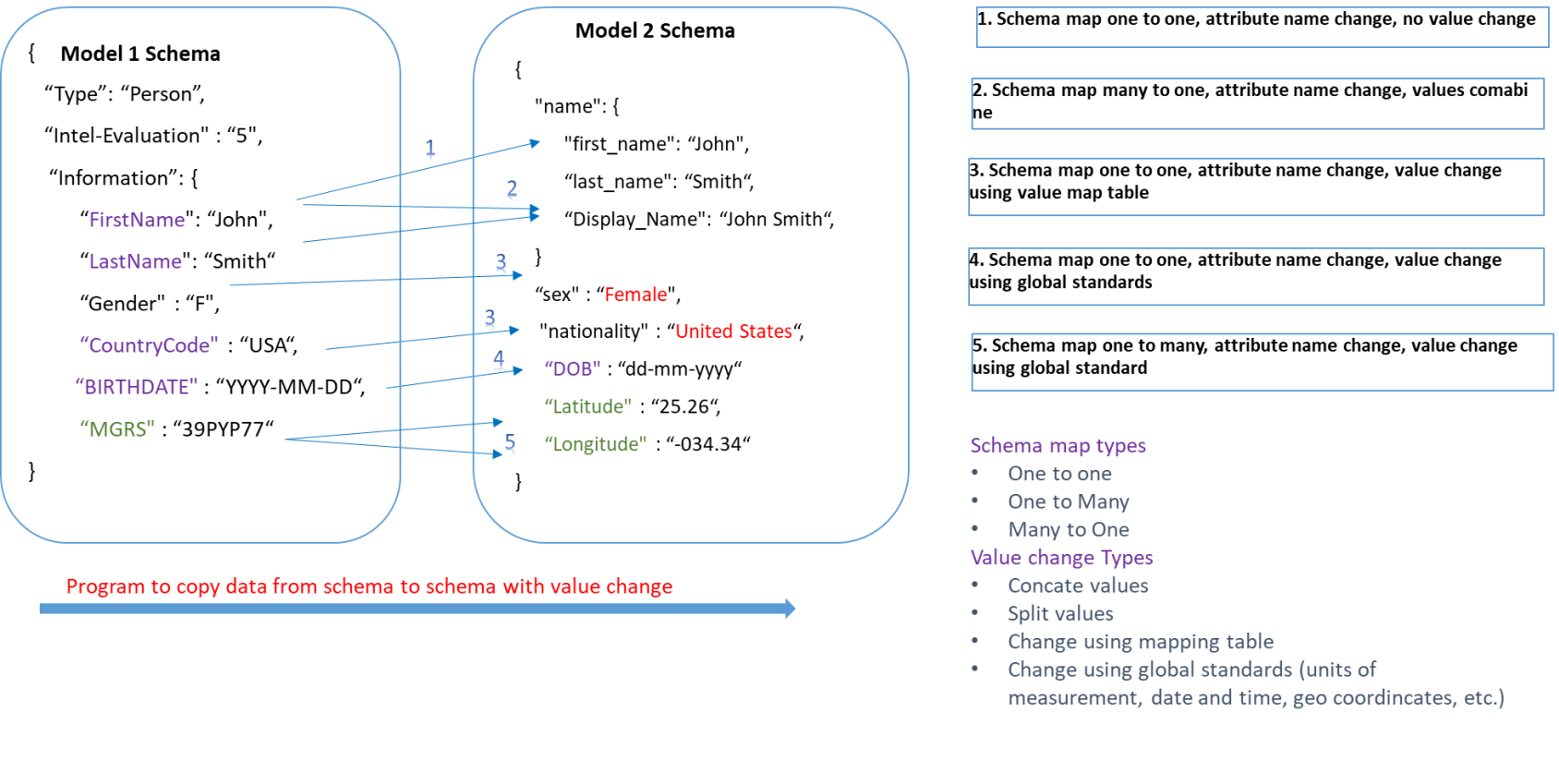
“FirstName": "John", --->["first_name": “John","Display_Name": "John Smith"]
"LastName": "Smith" --->"Display_Name": "John Smith",
"Gender" : "F", --->"sex" : "Female",
"MGRS" : "39PYP77" ---> ["Latitude" : "25.26","Longitude" : "-034.34"]
* Forested area restricts Maneuver
* Waterway restricts Maneuver
* (Ariana or IRA) has Capability of Tier 1 Chemical
* (Ariana or IRA) has Capability of Tier 1 air defense
* (Ariana or IRA) has Capability of Tier 1 armor
* The 62ID Area of Interest includes Country atropia
* The 62ID Area of Interest includes Country ariana
* The 62ID Area of Interest includes Country artzak
* Step 1 Receive the Mission
* Step 2 Mission Analysis
* Step 3 COA (courses of action) development
* Step 4 COA analysis
* Step 5 COA comparison
* Step 6 COA approval
* Step 7 Orders Production
Order
1.Situation
2. Mission
3. Service Support
5. Command & Signal
1. Situation
A. Enemy Forces
1. Weather and general forecast
2. Terrain
3.Enemy forces composition
4. Locations
5. Activity(attacking, retreating, defending, patrolling, etc.)
6. Strength, moreal equipment and capabilities
7. Probable course(s) of action when contractted (will they fight, disperse, retreat, attack)
B. Friendly Forces
1. Mission and concept of next higher unit
2. Location and planned actions of units to the left, right, front, and rear
3. Units provding fire support
(subject, predicate, object, plus location and time)
Complex assertion is answering 5 questions: who, what, where, when, and why
Mission statement
2nd PLT conducts an amush on Route Blue NLT(not later than) 1500 IOT(in-order-to) provide freedom of maneuver for the main element
Who? 2nd PLT
What? conducts an amush on
Where? Route Blue
When? NLT(not later than) 1500
Why? IOT(in-order-to) provide freedom of maneuver for the main element
Why? The answer to "why" reveals the commander's intent.
Complex assertion would need three SPO (subject predicate object) as below:
SPO 1:
Subject - 2nd PLT
Predicate - conducts an amush on
Object - Route Blue
Time - NLT(not later than) 1500 (date and time)
Location - Route Blue (coordinates)
SPO 2:
why - IOT(in-order-to) provide freedom of maneuver for the main element
Subject - main element
Predicate - should be provided
Object - freedom of maneuver
SPO 3:
SPO 1 has commander’s intent as SPO2
Or
SPO 1 (mission) supports SPO 2 (Commander’s intent)
* Add entity, add attributes for an entity, add relationship for an entity, Add relationship between two triples
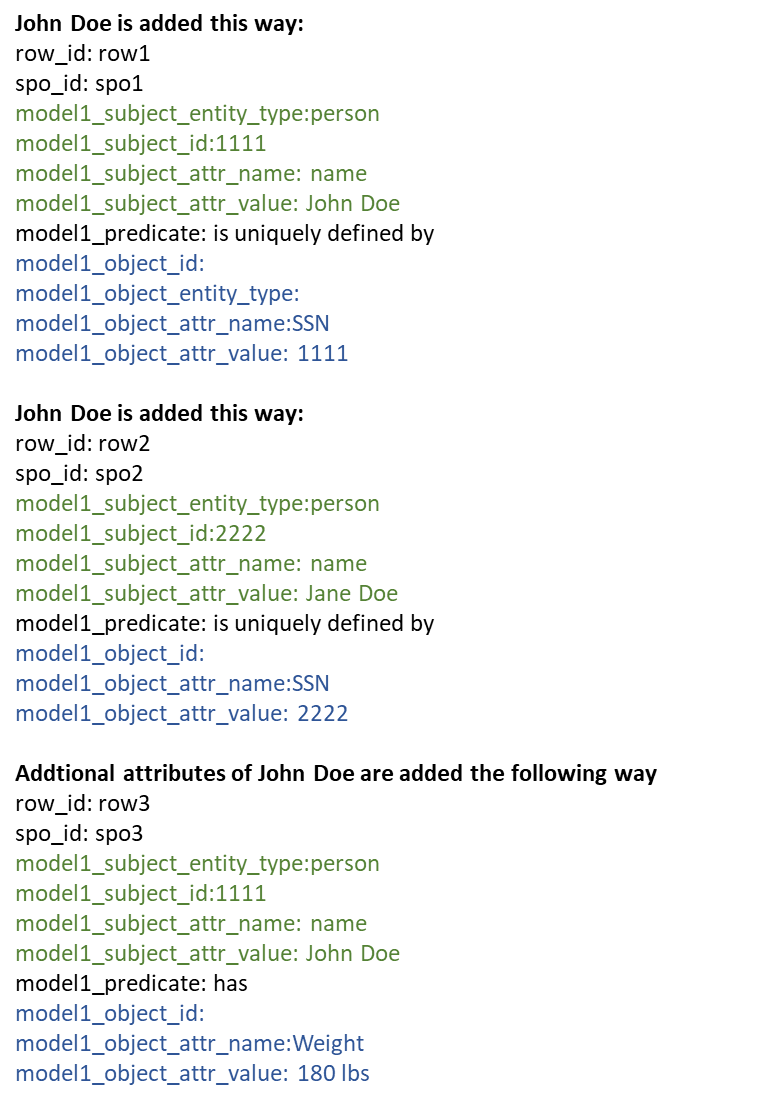

* Update current triple. Updates values of subject, predicate and object. No new ids are created.
* Insert new triple (treat current triple as template). This inserts new triple with attribute values on your screen. This will create new subject predicate and object ids.
* Refresh current triple after saving updates
* Use subject as your entity add attributes and or components for the subject. This inserts new triple with all subject id and new object ids
* Reset all values to blank so that you can update attributes as per your need
* Check categories if they are in model1
* Check categories if they are in model2
* Use current triple to create subject type triple and current triple id so triple to triple association can be added
* schema to schema - used for data transform from one app to another app
* schema to category - Typically used for lookup values
* source category to target category in a hierarchy - also known as value map during app to app data transform
* primary category hierarchy within a model - for drop down list, attribute definition at each level in hierarchy
* secondary category hierarchy within a model - reports or lookup by additional classification
* component category to assembly category with a model - category level definition of assembly or template
* component item to assembly item within a model - specific assembly that is derived from component category to assembly category with a model
* item to primary category - typical primary category assignment, attribute inheritance
* item to secondary category - reports or lookup by additional classification
* item to another item - mapping can be same as or similar to. Used for data transform from one app to another app